Introduction
Contents
Introduction#
Objective#
The objective of the oneAPI Unified Runtime is to provide a unified interface to device agnostic runtimes such as DPC++ across a wide variety of software platforms. The unified runtime provides extensibility where new backends can be developed to support new software platforms and devices. Software platforms can be enumerated through the interface and used to provide best experience. The interface will semantically align with the Level Zero Driver interface and support native platform access.
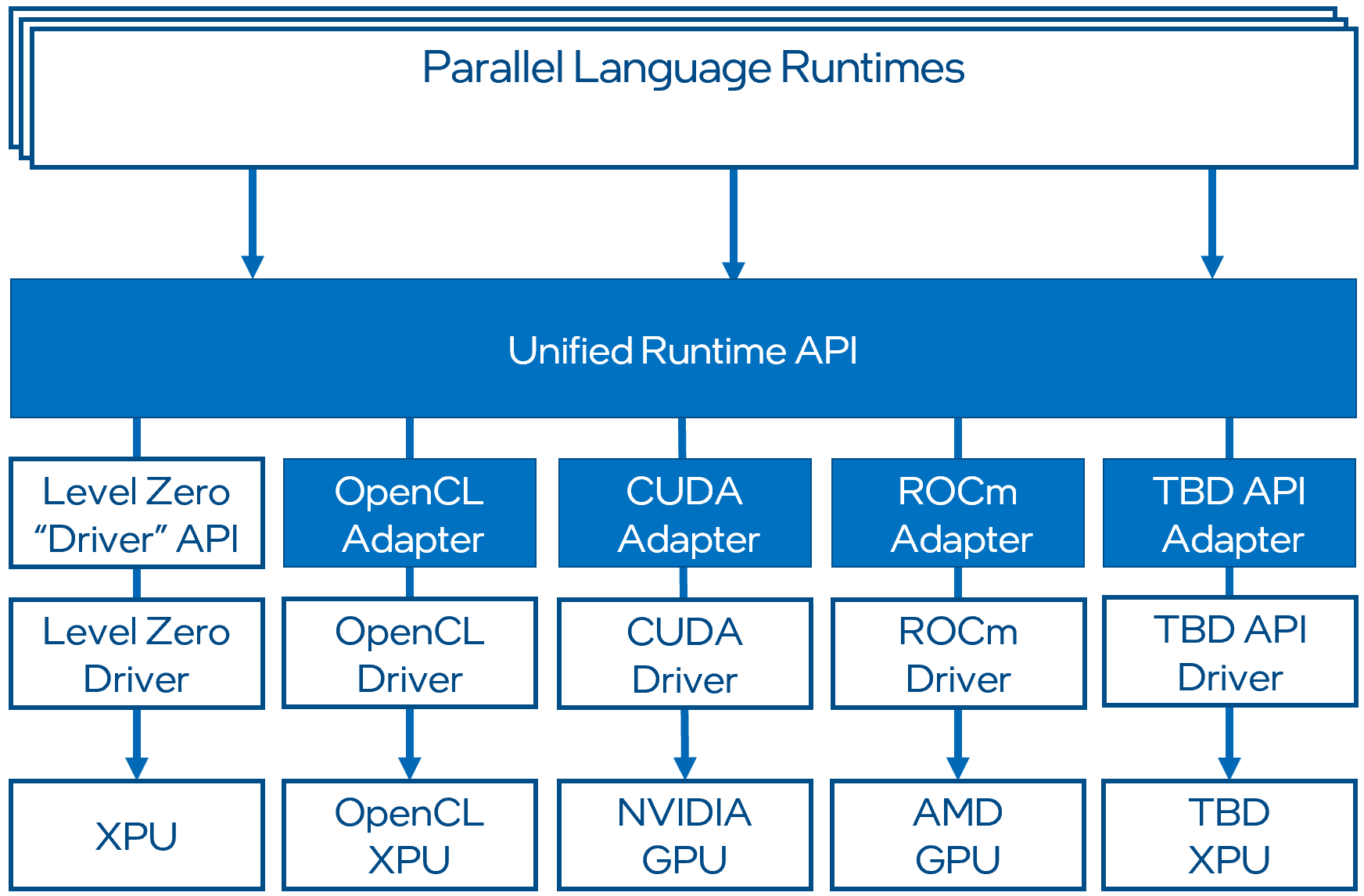
Fundamentals#
The following section provides fundamentals of the API design. For more detailed information, refer to the programming guides and detailed specification pages.
The repository for Unified Runtime can be found here:
Terminology#
This specification uses key words based on RFC2119 to indicate requirement level. In particular, the following words are used to describe the actions of an implementation of this specification:
May - the word may, or the adjective optional, mean that conforming implementations are permitted to, but need not behave as described.
Should - the word should, or the adjective recommended, mean that there could be reasons for an implementation to deviate from the behavior described, but that such deviation should be avoided.
Must - the word must, or the term required or shall, mean that the behavior described is an absolute requirement of the specification.
Versioning#
There are multiple versions that should be used by the application to determine compatibility:
Platform Version - this is the version of the API supported by the platform.
This is typically used to determine if the device supports the minimum set of APIs required by the application
There is a single 32-bit value that represents an entire collection of APIs
The value is encoded with 16-bit Major and 16-bit Minor parts
Major version increment consist of modified functionality, including deprecate features, and may break backwards-compatibility
Minor version increment consist of additional functionality, including promoted extensions, and must retain backwards-compatibility
The value is determined from calling urPlatformGetApiVersion
The value returned will be the minimum of the ur_api_version_t supported by the device and known by the driver
Error Handling#
The following design philosophies are adopted to reduce Host-side overhead:
By default, the driver implementation may not perform parameter validation of any kind
This should be handled by validation layer(s)
By default, neither the driver nor device provide may provide any protection against the following:
Invalid API programming
Invalid function arguments
Function infinite loops or recursions
Synchronization primitive deadlocks
Non-visible memory access by the Host or device
Non-resident memory access by the device
The driver implementation is not required to perform API validation of any kind
The driver should ensure well-behaved applications are not burdened with the overhead needed for non-behaving applications
Unless otherwise specified, the driver behavior is undefined when APIs are improperly used
For debug purposes, API validation can be enabled via the loader’s validation layer(s)
All API functions return ur_result_t
This enumeration contains error codes for the Unified Runtime APIs and validation layers
This allows for a consistent pattern on the application side for catching errors; especially when validation layer(s) are enabled
Multithreading and Concurrency#
The following design philosophies are adopted in order to maximize Host thread concurrency:
APIs are free-threaded when the runtime’s object handle is different.
the runtime should avoid thread-locks for these API calls
APIs are not thread-safe when the runtime’s object handle is the same, except when explicitly noted.
the application must ensure multiple threads do not enter an API when the handle is the same
APIs are not thread-safe with other APIs that use the same runtime’s object handle
the application must ensure multiple threads do not enter these APIs when the handle is the same
In general, the API is designed to be free-threaded rather than thread-safe. This provides multithreaded applications with complete control over both threading and locks. This also eliminates unnecessary runtime overhead for single threaded applications and/or very low latency usages.
The exception to this rule is that all memory allocation APIs are thread-safe since they allocate from a single global memory pool. If an application needs lock-free memory allocation, then it could allocate a per-thread pool and implement its own sub-allocator.
An application is in direct control over all Host thread creation and usage. The runtime should never implicitly create threads. If there is a need for an implementation to use a background thread, then that thread should be created and provided by the application.
Each API function must document details on the multithreading requirements for that call.
The primary usage-model enabled by these rules is:
multiple, simultaneous threads may operate on independent driver objects with no implicit thread-locks
driver object handles may be passed between and used by multiple threads with no implicit thread-locks
Application Binary Interface#
The Unified Runtime C APIs are provided to applications by a shared import library. C/C++ applications must include “ur_api.h” and link with “ur_api.lib”. The Unified Runtime C Device-Driver Interfaces (DDIs) are provided to the import library by the shared loader or runtime and driver libraries. C/C++ loaders and drivers must include “ur_ddi.h”.
The implementation of these libraries must use the default Application Binary Interface (ABI) of the standard C compiler for the platform. An ABI in this context means the size, alignment, and layout of C data types; the procedure calling convention. and the naming convention for shared library symbols corresponding to C functions. The ABI is backward-compatible for API minor version increments such as adding new functions, appending new enumerators, and using reserved bits in bitfields. ABI is not guaranteed to be backward-compatible for API major version increments such as modifying existing function signatures and structures, removing functions and structures, etc.
On platforms where Unified Runtime is provided as a shared library, library symbols beginning with “ur”, “urt” or “urs” and followed by a digit or uppercase letter are reserved for use by the implementation. Applications which use Unified Runtime must not provide definitions of these symbols. This allows the Unified Runtime shared library to be updated with additional symbols for new API versions or extensions without causing symbol conflicts with existing applications.
Tracing#
Unified Runtime loader implements tracing support through the XPTI framework.
Trace Point Type |
Parameter Description |
Metadata |
|---|---|---|
function_with_args_begin |
trace_type: xpti::trace_point_type_t::function_with_args_begin that marks the beginning of a function
parent: nullptr
event: nullptr
instance: Unique ID to allow the correlation of the function_with_args_begin event with the function_with_args_end event.
user_data: A pointer to function_with_args_t object, that includes function ID, name, and arguments.
|
None |
function_with_args_end |
trace_type: xpti::trace_point_type_t::function_with_args_end that marks the end of a function
parent: nullptr
event: nullptr
instance: Unique ID to allow the correlation of the function_with_args_end event with the function_with_args_begin event.
user_data: A pointer to function_with_args_t object, that includes function ID, name, arguments, and return value.
|
None |
Logging#
Logging in UR is handled by loggers which can be set for each library separately. There are several levels of logging: debug, info, warning, and error. The level of logging determines what messages will be printed, ie. the level set to warning means all messages at levels warning and error will be printed. By default, no messages are printed.
By default, there is a guarantee that error messages are flushed immediately. One can change this behavior to flush on lower-level messages.
Loggers redirect messages to stdout, stderr, or a file (default: stderr).
All of these logging options can be set with UR_LOG_LOADER and UR_LOG_NULL environment variables described in the Environment Variables section below. Both of these environment variables have the same syntax for setting logger options:
“[level:debug|info|warning|error];[flush:<debug|info|warning|error>];[output:stdout|stderr|file,<path>]”
- level - a log level, meaning that only messages from this level and above are printed,
possible values, from the lowest level to the highest one: debug, info, warning, error,
- flush - a flush level, meaning that messages at this level and above are guaranteed to be flushed immediately,
possible values are the same as above,
- output - indicates where messages should be printed,
possible values are: stdout, stderr and file, when providing a file output option, a <path> is required
Note
For output to file, a path to the file have to be provided after a comma, like in the example above. The path has to exist, file will be created if not existing. All these three logger options are optional. The defaults are set when options are not provided in the environment variable. Options have to be separated with ;, option names, and their values with :. Additionally, when providing file output, the keyword file and a path to a file have to be separated by ,.
An example of an environment variable for setting up the loader library logger with logging level set to info, flush level set to warning, and output set to
the out.log file:
UR_LOG_LOADER="level:info;flush:warning;output:file,out.log"
An example of an environment variable for setting up the null adapter library with logging level set to warning and output set to stdout:
UR_LOG_NULL="level:warning;output:stdout"
Adapter Discovery#
UR is capable of discovering adapter libraries in the following ways in the listed order:
Search in paths to the adapters set in UR_ADAPTERS_FORCE_LOAD environment variable.
All other adapter discovery methods are disabled when this environment variable is used.
Search in directories specified in UR_ADAPTERS_SEARCH_PATH environment variable.
Leave adapter discovery for the OS.
This method is disabled on Windows.
If on Linux, use the shared library discovery mechanism (see **ld.so**(8) for details).
Search in directory at the UR loader location.
Currently, UR looks for these adapter libraries:
ur_adapter_level_zero
For more information about the usage of mentioned environment variables see Environment Variables section.
Environment Variables#
Specific environment variables can be set to control the behavior of unified runtime or enable certain features.
- UR_LOG_LOADER#
Holds parameters for setting Unified Runtime loader logging. The syntax is described in the Logging section.
- UR_LOG_NULL#
Holds parameters for setting Unified Runtime null adapter logging. The syntax is described in the Logging section.
- UR_LOG_VALIDATION#
Holds parameters for setting Unified Runtime validation logging. The syntax is described in the Logging section.
- UR_ADAPTERS_FORCE_LOAD#
Holds a comma-separated list of library paths used by the loader for adapter discovery. By setting this value you can force the loader to use specific adapter implementations from the libraries provided.
Note
This environment variable should be used for development and debugging only.
Note
All other adapter discovery methods are disabled when this environment variable is used.
- UR_ADAPTERS_SEARCH_PATH#
Holds a comma-separated list of directory paths used for adapter discovery. By setting this value you can extend the list of directories the loader searches for adapter implementations.
Note
The usage of colons and semicolons is allowed only inside ‘’ or “” quote signs.
Note
This environment variable is ignored when
UR_ADAPTERS_FORCE_LOADenvironment variable is used.
- UR_ENABLE_VALIDATION_LAYER#
Holds the value
0or1. By setting it to1you enable validation layer.Note
This environment variable should be used for development and debugging only.
- UR_ENABLE_PARAMETER_VALIDATION#
Holds the value
0or1. By setting it to1you enable parameter validation for Unified Runtime API calls.Note
This environment variable should be used together with
UR_ENABLE_VALIDATION_LAYER.
- UR_ENABLE_LEAK_CHECKING#
Holds the value
0or1. By setting it to1you enable leak checking for Unified Runtime API calls involving object creation/destruction. Leak checking depends on the logging mechanism.Note
This environment variable should be used together with
UR_ENABLE_VALIDATION_LAYERandUR_LOG_VALIDATION.
Service identifiers#
Unified Runtime may create logs containing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in the form of unique device identifiers during its use. This capability is turned off by default. Please refer to the Logging and Environment Variables sections above for more information.